Embark on a journey into the realms of ecological connection and cosmic unity as we delve into the intriguing concept that is the Gaia hypothesis. Envision a world where our planet is not merely a collection of separate ecosystems, but a living, breathing entity in its own right. The Gaia hypothesis invites us to explore Earth as a complex, interconnected system where all living organisms, the atmosphere, and the geosphere are intricately intertwined. Join us as we unravel the mysteries and implications of this fascinating theory that challenges us to reconsider our relationship with the natural world.
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Gaia Hypothesis: Nature as a Living Organism
- Interconnectedness in the Gaia Hypothesis: Ecosystem Dynamics
- Implications of the Gaia Hypothesis on Environmental Conservation
- Applying Gaia Hypothesis Principles for Sustainable Living
- Q&A
- Final Thoughts
Understanding the Gaia Hypothesis: Nature as a Living Organism
The Gaia Hypothesis proposes that the Earth is a self-regulating system where life interacts with the atmosphere, oceans, and land to maintain conditions suitable for life. This fascinating concept suggests that the Earth itself can be seen as a living organism, with all its components working together in harmony.
By viewing the Earth as a single, self-regulating entity, the Gaia Hypothesis emphasizes the interconnectedness of all living and non-living parts of the planet. It invites us to consider how natural processes, such as the carbon cycle and climate regulation, are intricately linked and contribute to the overall balance of the Earth’s systems. This deeper understanding of nature can inspire us to respect and protect the delicate balance of our planet for the well-being of all life forms.

Interconnectedness in the Gaia Hypothesis: Ecosystem Dynamics
The Gaia Hypothesis proposes that the Earth functions as a self-regulating system where living organisms interact with the inorganic elements to maintain an environment conducive to life. This theory emphasizes the interconnectedness of all living and non-living components on Earth, highlighting the dynamic relationship between ecosystems and the planet itself.
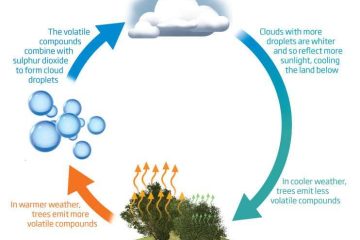
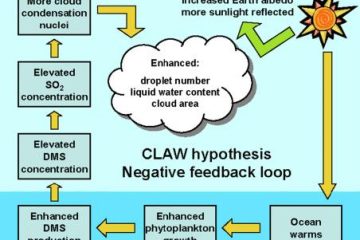
Within the framework of the Gaia Hypothesis, the concept of feedback loops plays a crucial role in understanding how ecosystems influence their own environment. **Positive feedback** mechanisms amplify changes, while **negative feedback** mechanisms work to stabilize the system. This delicate balance exemplifies the intricate web of interactions that sustain life on our planet, illustrating the harmonious dance between biotic and abiotic factors.

Implications of the Gaia Hypothesis on Environmental Conservation
Understanding the Gaia Hypothesis:
At its core, the Gaia Hypothesis proposes that the Earth functions as a self-regulating system, akin to a living organism. This theory suggests that the Earth’s biota, atmosphere, oceans, and soil interact to maintain conditions suitable for life. In essence, the planet is viewed as a single, complex entity where all components are interconnected and influence one another.
Implications for Environmental Conservation:
Embracing the Gaia Hypothesis can significantly impact how we approach environmental conservation. By recognizing the interconnectedness of all life forms and Earth systems, conservation efforts can be more holistic and effective. Understanding that small changes in one part of the ecosystem can have far-reaching consequences underscores the importance of preserving biodiversity and maintaining a balanced environment for the well-being of all species.

Applying Gaia Hypothesis Principles for Sustainable Living
Living in harmony with nature is essential for the well-being of our planet and future generations. The Gaia Hypothesis emphasizes the interconnectedness of all living organisms and the Earth itself. By applying the principles of this hypothesis to our daily lives, we can strive towards a more sustainable and balanced way of living.
One key aspect of the Gaia Hypothesis is promoting biodiversity and ecosystem health. By supporting diverse ecosystems, we ensure resilience against environmental changes and foster a thriving environment for all species. Additionally, recognizing and respecting the Earth as a complex, self-regulating system reminds us of our responsibility to protect and nurture this precious planet we call home. Embracing this mindset can guide us towards more sustainable practices, leading to a brighter and greener future for all.
Q&A
Q&A: Unveiling the Mysteries of the Gaia Hypothesis
Q: What is the Gaia Hypothesis all about?
A: The Gaia Hypothesis, proposed by scientist James Lovelock in the 1970s, suggests that the Earth itself can be viewed as a self-regulating organism. It posits that the biosphere and the physical components of the Earth are interconnected in a way that maintains the conditions necessary for life to thrive.
Q: How does the Gaia Hypothesis relate to the interconnectedness of Earth’s systems?
A: In essence, the Gaia Hypothesis highlights the intricate web of interactions between living organisms, the atmosphere, oceans, and the geology of the planet. It underscores how these components work together to create a stable environment conducive to life.
Q: Is the Gaia Hypothesis widely accepted in the scientific community?
A: While the Gaia Hypothesis has sparked both intrigue and debate since its inception, it has not been universally embraced by all scientists. Some view it as a thought-provoking concept that offers new perspectives on Earth’s ecosystems, while others remain skeptical of its implications.
Q: How does the Gaia Hypothesis influence our understanding of ecology and environmental conservation?
A: The Gaia Hypothesis encourages us to recognize the Earth as a complex, interconnected system that requires careful stewardship. By acknowledging the delicate balance between living organisms and their environment, we are prompted to consider the long-term effects of human activities on the planet.
Q: Are there real-world examples that support the principles of the Gaia Hypothesis?
A: From the regulation of atmospheric oxygen levels by plant life to the recycling of nutrients in ecosystems, numerous natural phenomena align with the principles of the Gaia Hypothesis. These examples serve as compelling illustrations of the interconnectedness and resilience of Earth’s systems.
Q: What can individuals do to align with the principles of the Gaia Hypothesis in their daily lives?
A: By adopting sustainable practices, supporting conservation efforts, and promoting environmental awareness, individuals can play a role in preserving the integrity of Earth’s interconnected systems. Small actions, when multiplied, can have a significant impact on fostering a harmonious relationship with our planet.
Final Thoughts
In a world where interconnectedness is key, the Gaia Hypothesis serves as a gentle reminder of our planet’s intrinsic harmony. As we delve deeper into the intricate web of life on Earth, let us embrace the profound wisdom that Gaia whispers to us through the rustling leaves, the gentle breeze, and the flowing rivers. May we continue to nurture and protect this beautiful home we call Gaia, for in her delicate balance lies the essence of our existence. Let us walk softly upon her surface, guided by the timeless wisdom of the Gaia Hypothesis.

0 Comments