In a world where interconnectedness reigns supreme, the Gaia Hypothesis assignment emerges as a beacon of contemplation and exploration. Delving into the intricate dance between the Earth and all its inhabitants, this assignment invites us to ponder the profound web of life that sustains our planet. Join us on a journey of discovery as we unravel the mysteries of Gaia and her intrinsic relationship with every living being. Let’s embark on a thought-provoking odyssey that promises to deepen our understanding of the delicate balance that shapes our world.
Table of Contents
- Exploring the Concept of Gaia Hypothesis in Environmental Studies
- Key Aspects of Gaia Hypothesis and its Implications for Ecosystems
- Analyzing Gaia Hypothesis in Practice: Practical Applications and Case Studies
- Recommendations for Embracing Gaia Hypothesis in Sustainable Practices
- Q&A
- Insights and Conclusions

Exploring the Concept of Gaia Hypothesis in Environmental Studies
Originating from the profound mind of James Lovelock, the Gaia Hypothesis is a riveting theory that poses the Earth as a self-regulating organism. By viewing the planet as a complex interconnected system, this hypothesis challenges conventional thoughts on the relationship between Earth and its inhabitants. Dive into the depths of environmental studies as we unravel the intriguing layers of Gaia.
Uncover the interconnectedness between all living and non-living entities on Earth, understanding how each component contributes to the delicate balance of our ecosystem. Explore the Gaia Hypothesis and embark on a journey of exploration into the symbiotic relationship between nature and humanity, shaping the world we inhabit in ways beyond imagination.
Key Aspects of Gaia Hypothesis and its Implications for Ecosystems
The Gaia Hypothesis proposes a fascinating perspective on the interconnectedness of Earth’s ecosystems, suggesting that the planet functions as a self-regulating organism. This concept, put forth by James Lovelock in the 1970s, implies that all living organisms, along with their inorganic surroundings, form a complex system that maintains conditions suitable for life. This holistic view challenges traditional scientific thinking by portraying Earth as a single, unified entity capable of regulating its own environment.
Implications of the Gaia Hypothesis extend beyond theoretical curiosity to practical considerations for ecosystem management and conservation efforts. By acknowledging the intricate web of relationships between living organisms and their environment, we gain insight into how human activities impact the delicate balance of nature. Understanding and respecting these interconnections becomes crucial in shaping sustainable practices that support biodiversity and overall ecosystem health. Embracing the principles of Gaia can guide us towards a more harmonious coexistence with the planet we call home.
Analyzing Gaia Hypothesis in Practice: Practical Applications and Case Studies
When exploring the Gaia Hypothesis firsthand, it becomes apparent how this concept transcends mere theory to offer practical insights across various disciplines. By delving into practical applications and intriguing case studies, we witness the intricate interconnectedness of our planet’s ecosystems. Through observation and analysis, researchers have uncovered compelling evidence supporting the interdependence of living organisms and their environment.
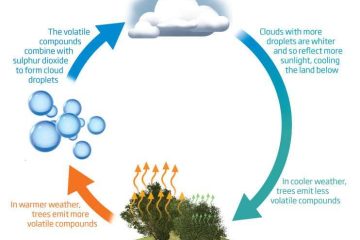
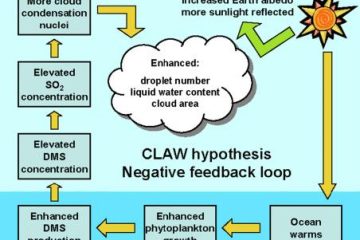
One fascinating case study showcases the remarkable symbiotic relationship between certain plant species and soil microorganisms in a delicate ecosystem. As these plants thrive, they release chemicals that influence the surrounding microorganisms, creating a harmonious balance that benefits all parties involved. This intricate web of interactions highlights the Gaia Hypothesis in action, illustrating the interconnected nature of life on Earth. Through real-world examples like this, we gain a deeper appreciation for the delicate balance that sustains our planet’s biodiversity.
Recommendations for Embracing Gaia Hypothesis in Sustainable Practices
When it comes to embracing the Gaia Hypothesis in sustainable practices, there are several key recommendations that can help align your efforts with this holistic approach to environmental stewardship.
Firstly, **prioritize biodiversity** in your initiatives. Supporting a diverse range of plant and animal species not only enhances ecosystem resilience but also fosters a healthier planet. Additionally, **incorporating regenerative agriculture** techniques can mimic natural systems, promoting soil health and carbon sequestration. By **engaging with local communities** and **advocating for policy changes** that promote sustainability, you can further contribute to the principles upheld by the Gaia Hypothesis.
Q&A
**Q&A: Exploring the Gaia Hypothesis Assignment**
Q: What is the Gaia Hypothesis?
A: The Gaia Hypothesis, proposed by James Lovelock in the 1970s, suggests that Earth functions as a self-regulating organism where living organisms interact with the environment to maintain conditions suitable for life.
Q: How does the Gaia Hypothesis assignment relate to this concept?
A: The Gaia Hypothesis assignment delves into exploring how human activities impact the delicate balance of Earth’s ecosystems and how individuals can contribute to restoring harmony between nature and society.
Q: What are some key points to consider when working on a Gaia Hypothesis assignment?
A: Students are encouraged to analyze the interconnectedness of living organisms, study the influence of human behavior on environmental sustainability, and propose actionable solutions to mitigate the negative impact of climate change.
Q: How can students approach researching for their Gaia Hypothesis assignment?
A: By conducting in-depth research on environmental trends, biodiversity conservation efforts, renewable energy solutions, and sustainable practices, students can gain valuable insights to support their arguments and recommendations.
Q: What are the potential benefits of completing a Gaia Hypothesis assignment?
A: Engaging in the Gaia Hypothesis assignment can enhance students’ critical thinking skills, raise awareness about environmental issues, foster a sense of responsibility towards nature, and inspire proactive measures to protect the planet for future generations.
Q: How can educators support students in fulfilling their Gaia Hypothesis assignment effectively?
A: Educators can provide resources, guidance on research methodologies, facilitate discussions on environmental ethics, and offer feedback to help students develop well-rounded perspectives and innovative solutions to address environmental challenges.
Insights and Conclusions
In conclusion, delving into the Gaia Hypothesis assignment has provided a fascinating journey into the intricate balance between Earth’s systems and life forms. As we explore the interconnectedness of our planet and its inhabitants, it becomes clear that we are all integral parts of a harmonious whole. Embracing the principles of Gaia can lead us to a deeper appreciation for the delicate relationship between humanity and the environment. Let us continue to nurture and protect our world, mindful of our role as stewards of Gaia’s intricate web of life. Together, we can strive towards a more sustainable future where harmony and balance reign supreme.

0 Comments