In the vast web of interconnected ecosystems that blanket our planet, lies a profound theory that whispers of a living Earth – the Gaia Hypothesis. This captivating concept, named after the Greek goddess of Earth, shifts our perception of our planet from a mere inanimate rock to a dynamic, self-regulating organism. Join us on a journey through the enigmatic realms of this hypothesis as we explore the intricate relationship between Earth’s biota, atmosphere, and geology, unveiling a tapestry of life that dances in harmonious balance.
Table of Contents
- Exploring the Intriguing Concept of the Gaia Hypothesis
- Unveiling the Interconnectedness of Earth’s Systems
- The Role of Feedback Mechanisms in Gaia Theory
- Implementing Sustainable Practices Inspired by the Gaia Hypothesis
- Q&A
- The Way Forward
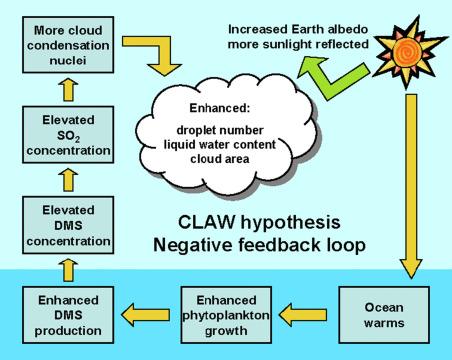
Exploring the Intriguing Concept of the Gaia Hypothesis
Imagine a world where the earth is not just a planet but a living, breathing organism in itself. This is the essence of the Gaia Hypothesis, a thought-provoking concept that suggests the Earth functions as a self-regulating system. According to this hypothesis, the Earth’s biosphere, atmosphere, oceans, and soil collaborate to maintain the conditions necessary for life to thrive.
One fascinating aspect of the Gaia Hypothesis is the idea that living organisms, including humans, play a vital role in shaping the environment and maintaining its equilibrium. Through intricate feedback mechanisms, the Earth and its inhabitants interact harmoniously, influencing each other in ways that sustain life on our planet. This interconnectedness highlights the delicate balance that exists within nature, underscoring the importance of preserving our environment for future generations.

Unveiling the Interconnectedness of Earth’s Systems
The intricate web of Earth’s interconnected systems is a mesmerizing tapestry that weaves together the delicate balance of life on our planet. From the vast oceans teeming with life to the lush forests breathing oxygen into the atmosphere, every element plays a crucial role in maintaining the harmony of Gaia, the living Earth. **Diving into the depths of this interconnectedness unveils a world where every action ripples through the entire ecosystem, showcasing the beauty of nature’s intricate design.**
As we explore the Gaia hypothesis, we uncover a perspective that views Earth as a self-regulating organism, where each component interacts to sustain life as a whole. The coalescence of the atmosphere, hydrosphere, lithosphere, and biosphere forms a symphony of interconnected systems, showcasing the awe-inspiring unity of our planet. Through this lens, we gain a deeper appreciation for the profound interconnectedness that governs the cycles of life, highlighting the delicate dance of energy and matter that sustains Earth’s vibrant ecosystems.
The Role of Feedback Mechanisms in Gaia Theory
The concept of Gaia Theory proposes that the Earth functions as a self-regulating system, akin to a living organism. Feedback mechanisms play a crucial role in maintaining the delicate balance necessary for life to thrive on our planet. These mechanisms operate like a symphony, with various components working together to ensure stability and sustainability over time.
One key feedback mechanism in Gaia Theory is the carbon cycle, where carbon is continuously exchanged between living organisms, the atmosphere, oceans, and the Earth’s crust. This cycle helps regulate the planet’s temperature and atmospheric composition, contributing to the overall health of Gaia. Additionally, homeostasis within ecosystems is maintained through feedback loops that adjust to external changes, allowing for adaptation and resilience in the face of environmental challenges. Through the intricate interplay of feedback mechanisms, Gaia Theory invites us to view Earth not just as a collection of separate parts, but as a complex, interconnected system that sustains life in remarkable ways.
| Feedback Mechanism | Role |
|---|---|
| Carbon Cycle | Regulates temperature and atmospheric composition |
| Homeostasis | Maintains ecosystem stability and resilience |

Implementing Sustainable Practices Inspired by the Gaia Hypothesis
Imagine a world where nature and technology work harmoniously together, mimicking the interconnectedness of ecosystems. allows us to envision such a future. By viewing the Earth as a complex, self-regulating system, we are prompted to reconsider our impact on the environment and strive for balance.
From utilizing renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power to promoting biodiversity in urban landscapes, there are numerous ways to embody the principles of Gaia in our daily lives. Embracing circular economy models, reducing waste generation, and advocating for green infrastructure are vital steps towards creating a more sustainable world for present and future generations.
Q&A
Q: What is the Gaia Hypothesis all about?
A: The Gaia Hypothesis, introduced by scientist James Lovelock in the 1970s, suggests that the Earth is a self-regulating system where living organisms interact with the atmosphere, oceans, and land to maintain conditions suitable for life.
Q: How does the Gaia Hypothesis differ from traditional views of the Earth?
A: Unlike traditional views that see Earth as a passive environment for life, the Gaia Hypothesis views the planet as a complex, interconnected system where life and the environment are inextricably linked.
Q: Can you give an example of how the Gaia Hypothesis works in nature?
A: One example of the Gaia Hypothesis in action is the regulation of oxygen levels in the atmosphere by living organisms such as plants and algae through processes like photosynthesis.
Q: What are the implications of the Gaia Hypothesis for environmental science?
A: The Gaia Hypothesis challenges us to see the Earth as a single, self-regulating entity, highlighting the importance of preserving biodiversity and maintaining the delicate balance of ecosystems for the well-being of all life forms.
Q: How has the scientific community responded to the Gaia Hypothesis?
A: The Gaia Hypothesis has sparked both excitement and skepticism within the scientific community, leading to further research and debate on the interconnectedness of life on Earth and the implications for our understanding of the planet.
The Way Forward
As we come to the end of this exploration into the fascinating concept of the Gaia hypothesis, let us reflect on the interconnectedness of all life on our planet. While scientific debate continues on the validity of Gaia as a living organism, its metaphorical power in emphasizing the delicate balance and intricate harmony of Earth’s systems remains undeniable.
Whether you find yourself marveling at the intricate dance of ecosystems or pondering the implications of humanity’s impact on Gaia, one thing is clear: our planet is a dynamic and resilient entity worthy of our deepest admiration and respect.
As we navigate the complexities of environmental issues and seek to forge a sustainable future for generations to come, may we draw inspiration from the Gaia hypothesis to nurture a greater sense of stewardship and reverence for the interconnected web of life that sustains us all. Thank you for joining us on this thought-provoking journey through the realms of Gaia.



0 Comments