Table of Contents
- Understanding the Gaia Theory and Its Implications for Climate Change
- The Role of Earths Biota in Regulating Climate Systems
- Interconnected Ecosystems: How Gaia Theory Sheds Light on Global Warming
- Practical Steps for Embracing Gaia Principles in Climate Action
- Innovative Solutions Inspired by Gaia Theory to Combat Climate Change
- Q&A
- Final Thoughts
Understanding the Gaia Theory and Its Implications for Climate Change
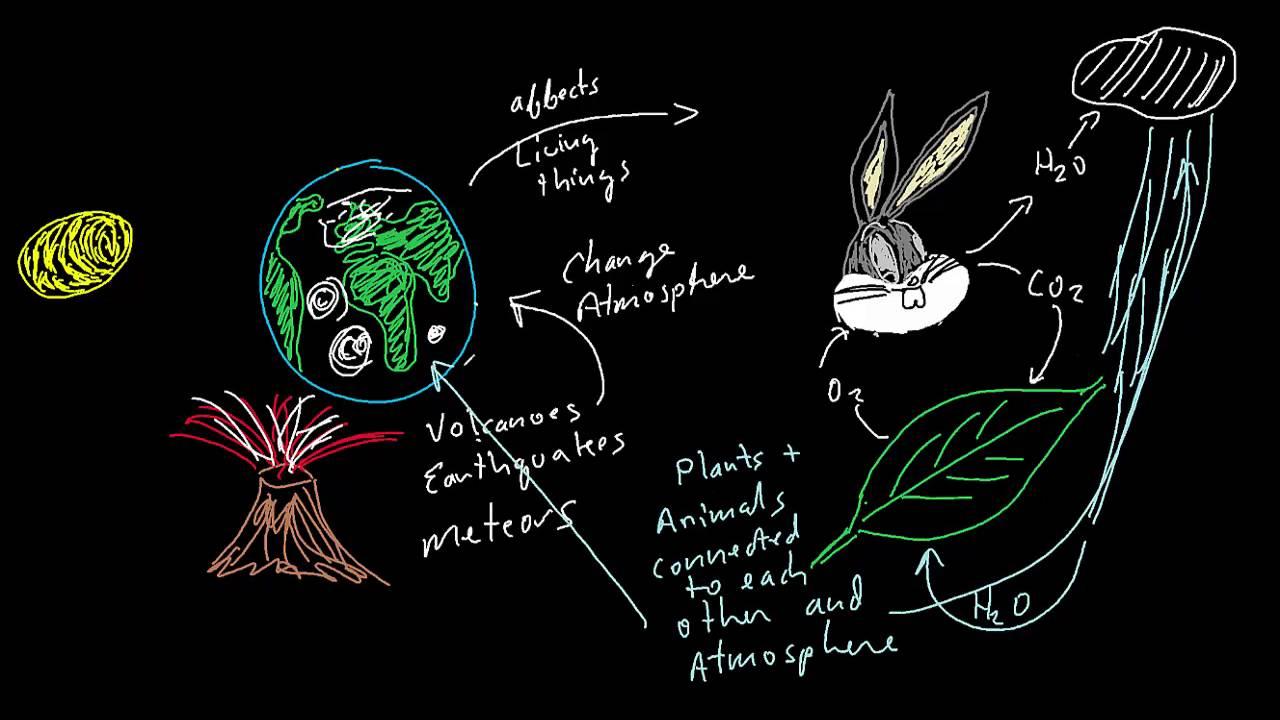
The Gaia Theory, proposed by James Lovelock in the 1970s, suggests that the Earth functions as a self-regulating system. This concept emphasizes that the biotic and abiotic components of our planet interact closely to maintain favorable conditions for life. At the heart of this theory is the idea that living organisms play a crucial role in regulating the environment, including the atmosphere, oceans, and soil. By understanding these intricate relationships, we can gain insight into how changes in climate may impact both the planet and its inhabitants.
One of the significant implications of this theory is the recognition that our actions can disrupt the delicate balance of Earth’s systems. As human activities such as deforestation, pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions increase, they throw the planet’s self-regulating mechanisms out of sync. For instance, rising temperatures, ocean acidification, and loss of biodiversity are clear outcomes of these disturbances, which not only harm ecosystems but also affect crucial services we depend upon, such as clean water and air. Therefore, accepting the interconnectedness highlighted by the Gaia Theory encourages us to reconsider our approach to environmental stewardship.
To effectively address climate change, it is essential to adopt sustainable practices that align with Gaia’s principles. Actionable strategies may include:
- Restoring natural habitats to support biodiversity
- Implementing renewable energy solutions to reduce carbon footprints
- Promoting sustainable agriculture that enhances soil health
- Encouraging community-based initiatives for environmental education
By fostering a deeper comprehension of Gaia Theory and its implications, we equip ourselves with the knowledge needed to advocate for policies and practices that protect our planet and ensure its resilience against the growing threats posed by climate change.
The Role of Earths Biota in Regulating Climate Systems
The intricate tapestry of life on Earth plays a pivotal role in maintaining the planet’s climate systems. Various organisms, from the tiniest microbes to towering trees, contribute to the regulation of atmospheric gases, carbon cycles, and temperature stability. Through processes such as photosynthesis, respiration, and decomposition, these biological entities help to balance the levels of greenhouse gases and other crucial elements that influence climate patterns.
Key functions of living organisms in climate regulation include:
- Carbon Sequestration: Plants absorb CO2 during photosynthesis, storing carbon in their biomass and soil, effectively reducing atmospheric CO2 levels.
- Soil Maintenance: Soil microorganisms play a vital role in nutrient cycling and soil health, impacting water retention and erosion, thus influencing local climates.
- Climate Feedbacks: The interactions between organisms and their environment generate feedback mechanisms that can amplify or dampen climatic shifts.
The diversity of life forms enables ecosystems to respond dynamically to environmental changes. Coral reefs, forests, and wetlands serve not only as carbon sinks but also as biodiversity reservoirs, enhancing resilience against climate disruptions. Additionally, the loss of species can lead to the destabilization of these natural processes, resulting in feedback loops that exacerbate climate change effects. Understanding the interplay between Earth’s biota and climate systems is crucial for developing effective conservation and restoration strategies aimed at mitigating climate impacts.
Interconnected Ecosystems: How Gaia Theory Sheds Light on Global Warming
The Gaia Theory presents a compelling framework for understanding the intricate relationships within Earth’s ecosystems and their contribution to climate regulation. At its core, this theory suggests that the Earth functions as a single, self-regulating entity, where living organisms and their inorganic surroundings are interconnected. This interconnectedness implies that any disruption in one component can reverberate throughout the entire system, leading to significant consequences for global climate. For example, the following factors illustrate the complexity of these relationships:
- Biological Feedback Loops: Organisms like phytoplankton produce vast amounts of oxygen, while plants sequester carbon. These processes not only support life but also help regulate atmospheric conditions.
- Soil Health: Healthy soils are vital for carbon storage. When soil is disturbed, it can release carbon back into the atmosphere, exacerbating climate change.
- Gas Emissions: Methane and carbon dioxide released by living organisms and industries can trap heat, leading to a rise in global temperatures.
Understanding these relationships highlights the potential for sustainable practices to mitigate climate change. By adopting approaches that harmonize agricultural practices with natural ecosystems, significant strides can be made to reduce the human footprint on the planet. For instance, regenerating forests can enhance biodiversity, improve soil health, and maintain carbon sinks. The importance of these actions can be summarized in the following table:
| Action | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Reforesting | Increases carbon absorption |
| Sustainable farming | Enhances soil quality |
| Conserving wetlands | Regulates water levels |
As climate change continues to pose a significant threat, the Gaia Theory emphasizes the urgency of fostering a healthier planet through holistic approaches. By recognizing our role within this interconnected web of life, we can better appreciate the impact of our actions and galvanize collective efforts to protect our environment. The solution to global warming is not merely mitigation but rather the restoration of balance within the Earth’s systems, ensuring that they can thrive for generations to come.
Practical Steps for Embracing Gaia Principles in Climate Action
Adopting Gaia principles in climate action involves recognizing the interconnectedness of life and our dependence on the Earth’s ecosystems. This holistic view encourages individuals and organizations to take a step back and evaluate their impact on the planet. To effectively embrace these principles, consider the following practical steps:
- Foster Biodiversity: Protecting diverse species allows ecosystems to thrive. Start by supporting local conservation efforts or creating a garden that encourages native plants and wildlife.
- Reduce Waste: Practice the three Rs—reduce, reuse, recycle. This not only minimizes landfill waste but also conserves resources and reduces pollution.
- Support Sustainable Practices: Choose products and services from companies that practice sustainability. Look for certifications such as Fair Trade or organic to ensure your choices align with Gaia principles.
Community engagement is vital in propagating the values aligned with Gaia principles. Forming or joining local groups focused on environmental advocacy can amplify your impact. Here are some effective community action ideas:
- Organize Clean-Up Events: Gather a group of volunteers to clean parks, beaches, or local streets. This fosters community spirit and raises awareness about pollution.
- Hold Workshops: Educate your community about sustainable living, gardening, or climate action strategies. Knowledge is power, especially when shared collectively.
- Advocate for Policy Change: Work with local governments to promote environmental policies that protect natural resources and reduce carbon emissions.
Educating oneself and others about Gaia principles is essential for long-term commitment and action. Schools and organizations can incorporate these teachings into their curriculums and practices. Consider this simple framework:
| Gaia Principle | Actionable Strategy |
|---|---|
| Interconnectedness | Promote interconnected eco-networks through workshops and discussions. |
| Holistic Approach | Integrate environmental studies across various subjects for comprehensive learning. |
| Resilience | Create projects that enhance community resilience against climate effects. |

Innovative Solutions Inspired by Gaia Theory to Combat Climate Change
The concept that Earth functions as a single, self-regulating organism opens up a wealth of innovative strategies to tackle the pressing issue of climate change. By observing the interconnectedness of ecosystems as suggested by Gaia Theory, we can implement solutions that mirror natural processes. For instance, urban forestry initiatives can replicate natural biodiversity, improving air quality and supporting local wildlife. This approach not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of urban areas but also mitigates the urban heat island effect. As cities expand, planting native trees and vegetation can create vital green corridors that sustain biodiversity while absorbing carbon emissions.
Another compelling solution lies in the realm of sustainable agriculture, driven by the principles of ecological balance. Implementing permaculture practices encourages the cultivation of crops in symbiotic relationships, reducing the need for chemical fertilizers and pesticides. By fostering interdependent farming systems, communities can produce food while restoring soil health and increasing local resilience to climate impacts. Additionally, agroforestry systems can enhance carbon sequestration, enriching both the land and the livelihoods of farmers. Embracing these practices can lead to a more sustainable food system that nourishes people while nurturing the planet.
Furthermore, harnessing advanced technology inspired by Gaia’s principles—such as biomimicry—can unveil breakthrough innovations. For example, designing energy-efficient buildings that mimic natural ventilation systems can drastically reduce energy consumption. This approach not only decreases greenhouse gas emissions but also creates healthier indoor climates for inhabitants. The integration of renewable energy sources, inspired by natural energy cycles, further exemplifies how innovative technologies can align with Gaia’s vision, providing sustainable energy solutions to power our future. Emphasizing collective responsibility and interconnectedness, these strategies pave the way for resilience against climate change.



0 Comments