Nestled within the ivy-clad walls of Harvard University lies a fascinating theory that intertwines science and philosophy, known as the Gaia hypothesis. This captivating concept proposes that the Earth is a self-regulating organism, akin to a living being. Join us on a journey of exploration as we unravel the intriguing facets of the Gaia hypothesis and delve into the thought-provoking discussions taking place at one of the world’s most prestigious academic institutions. Welcome to the intersection of academia and nature’s mysteries at Harvard – where the Gaia hypothesis thrives.
Table of Contents
- Unveiling the Gaia Hypothesis: Exploring its Origins and Evolution
- Harvard’s Perspective on the Gaia Hypothesis: Research and Contributions
- Critique and Controversies Surrounding the Gaia Hypothesis at Harvard
- Embracing the Gaia Hypothesis: Implementing Sustainable Practices for a Balanced Future
- Q&A
- The Way Forward
Unveiling the Gaia Hypothesis: Exploring its Origins and Evolution
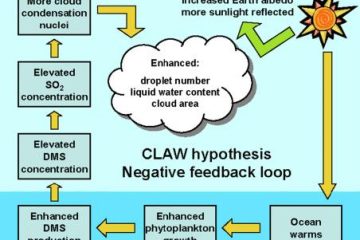
The Gaia Hypothesis, named after the Greek goddess of the Earth, posits a fascinating concept of our planet functioning as a single, self-regulating organism. Initially proposed by scientist James Lovelock and biologist Lynn Margulis in the 1970s, this revolutionary idea challenges conventional views of Earth as a passive environment but rather as a dynamic system capable of maintaining life. Through a delicate balance of interactions between living organisms and their environment, Gaia Theory suggests that the Earth’s biosphere, atmosphere, oceans, and soil are interconnected and work together to create a harmonious ecosystem.
Over the years, the Gaia Hypothesis has sparked intense debates and inspired further research into understanding the intricate web of life on our planet. By viewing Earth as a living entity with a collective consciousness, proponents of the Gaia Theory advocate for a deeper appreciation of the interconnectedness of all life forms. Through collaborative efforts and environmental stewardship, the Gaia Hypothesis offers a unique perspective on how humanity can coexist with the Earth sustainably. Embracing the idea of Gaia as a self-regulating system can lead to innovative solutions for environmental challenges and promote a sense of interconnectedness and responsibility towards our planet’s well-being.
| Key Points | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Earth as a self-regulating organism | Encourages environmental stewardship |
| Interconnectedness of all life forms | Promotes sustainability |
| Collaborative efforts for Earth’s well-being | Innovative solutions for environmental challenges |

Harvard’s Perspective on the Gaia Hypothesis: Research and Contributions
Harvard’s perspective on the Gaia hypothesis sheds light on the intricate relationship between Earth and its living organisms. Researchers at Harvard have delved into the theory that the Earth functions as a single, self-regulating system, maintaining conditions favorable for life.
Through comprehensive studies and innovative research initiatives, Harvard has contributed significantly to the understanding of Gaia’s implications on ecology, climate, and sustainability. The university’s findings have sparked further exploration into the interconnectedness of life forms and the environment, highlighting the profound impact of Gaia on shaping our planet’s dynamics and resilience.
Critique and Controversies Surrounding the Gaia Hypothesis at Harvard
When discussing the Gaia Hypothesis at Harvard, it’s essential to address the various critiques and controversies that surround this intriguing concept. While the Gaia Hypothesis proposes that the Earth functions as a self-regulating organism, maintaining conditions conducive to life, it has sparked debates among scientists and scholars.
<p>One of the primary points of contention is whether the Earth can truly be considered as a single, self-regulating entity or if it's more accurate to view the planet as a complex system of interconnected components. Additionally, debates arise regarding the degree of intentionality implied by the Gaia Hypothesis – whether Earth's systems truly act in a purposeful manner or if they simply exhibit emergent behavior.</p>
Embracing the Gaia Hypothesis: Implementing Sustainable Practices for a Balanced Future
In a world where environmental sustainability is gaining momentum, the Gaia Hypothesis serves as a guiding light towards a harmonious coexistence between humans and Earth. The essence of this hypothesis lies in the interconnectedness of all living organisms with the planet itself, embodying a symbiotic relationship that emphasizes balance and preservation. By embracing the Gaia Hypothesis, societies can pave the way towards a more sustainable future by implementing practices that nurture, protect, and respect the delicate ecosystems that support life as we know it.
Key Practices to Implement Sustainable Gaia Principles:
- Cultivating organic farming methods to promote soil health and biodiversity.
- Adopting renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power to reduce carbon footprint.
- Supporting local communities through fair trade practices to enhance economic resilience.
- Embracing circular economy initiatives to minimize waste and maximize resource efficiency.
| Sustainable Practices | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Organic Farming | Improved soil fertility and reduced chemical pollution |
| Renewable Energy Sources | Lower greenhouse gas emissions and energy independence |
| Fair Trade Practices | Empowerment of local producers and ethical supply chains |
| Circular Economy Initiatives | Reduced resource waste and increased sustainability |
Q: What is the Gaia Hypothesis and why is it significant?
A: The Gaia Hypothesis proposes that the Earth is a self-regulating system where living organisms interact with their inorganic surroundings, maintaining conditions that are suitable for life. It suggests that the Earth functions as a single organism, named after the Greek goddess of the Earth, Gaia.
Q: How does the Gaia Hypothesis relate to Harvard University?
A: Harvard University has been a hub for pioneering research and discussions around the Gaia Hypothesis, with various faculties and researchers delving into its implications for ecology, climate science, and sustainability.
Q: Who are some notable researchers at Harvard involved in Gaia Hypothesis studies?
A: Scientists like James Lovelock and Lynn Margulis have made significant contributions to the development and exploration of the Gaia Hypothesis at Harvard, shaping our understanding of the interconnectedness of life on Earth.
Q: What are some key debates surrounding the Gaia Hypothesis within the academic community?
A: While the Gaia Hypothesis has sparked intriguing discussions about the Earth’s interconnected systems, there are ongoing debates about the extent to which the Earth can be considered a single self-regulating organism and how it influences our approach to environmental challenges.
Q: How can individuals engage with the concepts of the Gaia Hypothesis in their daily lives?
A: Understanding the principles of the Gaia Hypothesis can inspire individuals to adopt more sustainable practices, appreciate the intricate balance of ecosystems, and advocate for policies that prioritize the well-being of our planet.
The Way Forward
As we conclude this exploration into the fascinating realm of the Gaia hypothesis at Harvard, we invite you to ponder the intricate interconnectedness of our planet and all its living inhabitants. From the lecture halls of Harvard to the far-reaching implications of Gaia theory, we hope this article has sparked a newfound curiosity within you. Let us continue to marvel at the wondrous beauty of Earth and strive to preserve its delicate balance for generations to come. Thank you for joining us on this enlightening journey. Embrace the wisdom of Gaia, for in understanding her, we may just uncover the secrets to a sustainable future.


0 Comments