Table of Contents
- Exploring the Interconnection Between Ecosystems and Human Well-Being
- Understanding the Impact of Climate Change on Global Health
- Innovative Solutions for Sustainable Resource Management
- Empowering Communities Through Environmental Education
- Strategies for Strengthening Policies in Environmental Health
- Q&A
- Final Thoughts
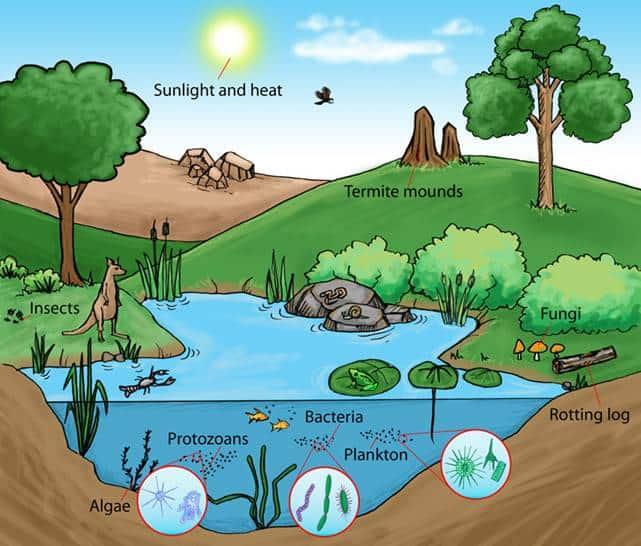
Exploring the Interconnection Between Ecosystems and Human Well-Being
In the intricate dance of nature and human life, ecosystems play a pivotal role in sustaining our health and well-being. These natural systems provide us with essential services such as clean air, potable water, and fertile soil, forming the backbone of agricultural productivity and food security. Beyond these tangible resources, ecosystems also offer cultural and recreational benefits, fostering mental health and a sense of connection to the natural world. Understanding the depth of these interconnections prompts us to appreciate the value of sustainable practices, which aim to preserve these vital ecosystem services for future generations.
One of the most compelling relationships between ecosystems and human health is their role in disease regulation. Natural habitats regulate populations of disease vectors, such as mosquitoes and ticks, lowering the incidence of illnesses like malaria and Lyme disease. Biodiverse ecosystems tend to be more resilient, reducing the risk of zoonotic diseases, which arise from animals and can be transmitted to humans. Consider the following roles ecosystems play in disease management:
- Vector Control: Natural predators manage vectors, reducing disease transmission.
- Water Purification: Wetlands filter pathogens, ensuring safer water supplies.
- Environmental Stabilization: Diverse species provide checks and balances on potential disease carriers.
Economically, the support ecosystems offer is invaluable yet often underestimated. They contribute not only through direct resources but also by enhancing resilience against climate impacts and natural disasters. Investing in ecosystem conservation can yield significant economic benefits, as revealed by the table below:
| Service | Annual Global Contribution (USD) |
|---|---|
| Pollination | $235 billion |
| Water Filtration | $9.2 billion |
| Climate Regulation | $3.1 trillion |
As we venture deeper into understanding how ecosystems interface with human well-being, it becomes increasingly clear that safeguarding these natural systems is not only a responsibility but a necessity for our survival and prosperity.

Understanding the Impact of Climate Change on Global Health
The complex relationship between environmental transformations and human health is becoming increasingly evident as these changes intensify across the globe. The alterations in climate patterns lead to severe weather events, rising sea levels, and shifts in ecosystems, each contributing uniquely to health challenges. For example, more frequent and severe heatwaves are associated with heat stress and related illnesses, particularly affecting vulnerable populations like the elderly and children. In areas where temperatures are climbing steadily, we see an uptick in the spread of vector-borne diseases such as malaria and dengue fever. These diseases thrive in warmer climates, thus broadening their range and affecting populations previously untouched by such health threats.
Moreover, food security is deeply intertwined with climate dynamics. Droughts, floods, and unpredictable weather patterns disrupt agricultural production, compounding issues of malnutrition and hunger, especially in regions heavily reliant on subsistence farming. A shift in food availability not only leads to direct nutritional challenges but also impacts economic stability in affected areas. In addition, as oceans absorb more carbon dioxide, we witness ocean acidification, which affects marine life and consequently the communities depending on those resources. Coastal populations find their food sources directly compromised, leading to cascading effects on health and economic sustenance. Understanding these interdependencies is critical for developing adaptive strategies to curb negative impacts on food systems.
Urban areas, too, are not spared, as increased pollution levels and poor air quality accompany urban growth related to climate change. Respiratory illnesses, including asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, are exacerbated by pollutants that thrive in warmer, stagnant air masses. Cities often face compounding issues of heat island effects, where urban areas become significantly warmer than their rural counterparts. This heat progression influences societal productivity and quality of life, driving public health initiatives to mitigate detrimental effects. The inherent complexity and scope of climate-induced health impacts necessitate a holistic approach in policy-making and community planning, ensuring environmental sustainability and human well-being are aligned.
Innovative Solutions for Sustainable Resource Management
- Hydroponics and Vertical Farming: Allow urban centers to grow fresh produce, minimizing transportation emissions.
- Biodegradable Plastics: Innovations in materials science lead to plastics that decompose naturally, posing less risk to ecosystems.
- Energy Efficient Building Designs: Aim to optimize natural light and insulation, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.

Empowering Communities Through Environmental Education
The journey towards nurturing a healthier planet is intricately linked to how well communities understand and value their environment. Environmental education plays a pivotal role in cultivating a sense of stewardship among individuals, inspiring them to advocate for sustainable practices. By imparting knowledge about ecosystems, biodiversity, and conservation strategies, communities can better appreciate the intricate balance required to maintain planetary health. These educational initiatives not only encourage responsible behavior but also empower locals to engage in impactful environmental decision-making.
Key Benefits of Environmental Education:
- Increased Awareness: Provides deeper understanding of ecological issues, fostering informed and conscious citizens.
- Community Engagement: Encourages collective efforts in addressing environmental challenges, promoting grassroots movements.
- Sustainability Practices: Equips inhabitants with the tools and knowledge necessary to implement greener habits in daily life.
By embracing environmental education, communities can drive a wave of positive change, one that not only reconstructs local habitats but also contributes to a global movement towards planetary resilience. When communities place importance on ecological health as a priority, they unlock the potential for innovation — from local green businesses to community-led conservation projects. This transformation can be solidified through partnerships with educational institutions, non-profits, and governmental bodies, creating a comprehensive support system for widespread environmental literacy. The result is a future where sustainable living is not just a choice, but a shared community success story.

Strategies for Strengthening Policies in Environmental Health
Implementing effective measures requires thorough analysis and collaboration among stakeholders. Conducting comprehensive risk assessments can help identify potential hazards and prioritize issues. Additionally, fostering a culture of interdisciplinary collaboration ensures that public health professionals, scientists, and policymakers work together towards common goals. By establishing forums for regular dialogue, these groups can share insights, discuss recent developments, and adapt strategies more effectively.
One crucial component is strengthening community engagement to ensure policies are not only well-designed but also supported at the grassroots level. Encouraging participation through educational programs and public consultations can cultivate a more informed citizenry. Furthermore, communities can be empowered to participate in monitoring environmental health changes actively, thus providing valuable feedback. Incorporating local knowledge into the decision-making process helps craft policies that are more sustainable and contextually appropriate.
Effective monitoring and evaluation frameworks are vital for continuously improving policy outcomes. Utilizing data visualization tools can enhance the understanding and communication of complex environmental health data. These tools should be designed to present information in an accessible manner, fostering transparency and accountability. Incorporating these strategies into a cohesive policy approach not only strengthens current practices but paves the way for innovative solutions. The following table showcases some critical tools for policy enhancement:
| Tools | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Risk Assessment Software | Identifies hazards and prioritizes interventions |
| Data Visualization Platforms | Improves clarity and stakeholder communication |
| Community Feedback Systems | Incorporates local insights into decision-making |



0 Comments