Step into the world of environmental philosophy and scientific speculation as we delve into the intriguing concept of the Gaia Hypothesis. This theory, proposed by the renowned scientist James Lovelock, presents a perspective on Earth as a self-regulating and interconnected system, akin to a living, breathing entity. Join us on a journey through time and discovery as we explore the origins, evolution, and implications of the Gaia Hypothesis.
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Gaia Hypothesis and Its Origins
- Exploring the Significance of James Lovelock’s Theory
- Implications of the Gaia Hypothesis on Environment and Ecology
- Incorporating Gaia Hypothesis Principles for Sustainable Living
- Q&A
- In Conclusion

Understanding the Gaia Hypothesis and Its Origins
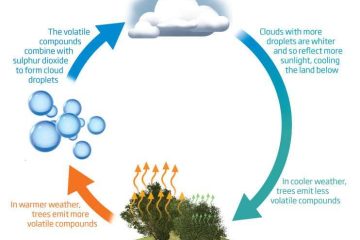
The concept of the Gaia Hypothesis, proposed by scientist James Lovelock, suggests that the Earth functions as a self-regulating organism, maintaining conditions suitable for life through complex interactions between the biosphere, atmosphere, hydrosphere, and lithosphere. This theory views Earth as a single, interconnected system where living organisms and their inorganic surroundings co-evolve.
At the core of the Gaia Hypothesis lies the idea that the Earth operates like a living organism, displaying characteristics of homeostasis and feedback mechanisms. This paradigm shift in understanding our planet challenges traditional views of Earth as a passive environment, highlighting the dynamic and interdependent nature of all life forms and their environment.
Exploring the Significance of James Lovelock’s Theory
Intriguing insights lie within James Lovelock’s Gaia hypothesis, a concept that delves into the interconnectedness of Earth’s systems and life forms. The theory proposes that the Earth operates as a self-regulating organism, where biological processes subtly influence the environment to maintain conditions suitable for life. This profound idea challenges conventional perspectives on the planet and sparks contemplation about humanity’s relationship with nature.
As we venture into the realm of Lovelock’s theory, we uncover a perspective that portrays Earth as a living entity with complex feedback mechanisms. The Gaia hypothesis underscores the delicate balance between life and the environment, highlighting the intricate dance of ecosystems working in harmony. By recognizing the interconnected nature of all living beings, we gain a deeper appreciation for the planet’s resilience and the importance of stewardship for future generations.
Implications of the Gaia Hypothesis on Environment and Ecology
The Gaia hypothesis, a captivating concept that suggests Earth functions as a self-regulating organism, has sparked profound discussions within the scientific community. This intriguing idea proposes that the biosphere and environment on our planet are delicately interconnected, forming a complex and dynamic system that maintains the conditions necessary for life to thrive. One implication of the Gaia hypothesis is the recognition that all living organisms, from the tiniest microorganisms to the largest mammals, play crucial roles in shaping and sustaining the Earth’s environment.
This holistic viewpoint emphasizes the importance of biodiversity in maintaining ecological balance and resilience. By acknowledging the interdependence of species and ecosystems, the Gaia hypothesis encourages a deeper understanding of the intricate web of life on Earth. This perspective highlights the significance of conservation efforts and sustainable practices to preserve the delicate harmony of our planet. Embracing the principles of interconnectedness and co-existence can lead to innovative approaches in environmental protection and management, fostering a healthier and more sustainable future for all living beings.
Incorporating Gaia Hypothesis Principles for Sustainable Living
Embracing the essence of the Gaia Hypothesis in everyday sustainable practices can lead to a harmonious coexistence with our planet. By acknowledging the interconnectedness of all living beings and the Earth itself, we can cultivate a more conscious and ecologically responsible way of life.
<p>**Here are some practical ways to incorporate Gaia Hypothesis principles into your daily routine:**</p>
<ul>
<li>**Mindful Consumption**: Opt for reusable products and reduce waste to minimize your ecological footprint.</li>
<li>**Natural Energy Sources**: Harness solar or wind power to decrease reliance on non-renewable energy.</li>
<li>**Regenerative Agriculture**: Support local farmers practicing sustainable agriculture for a healthier ecosystem.</li>
</ul>Q&A
Title: Exploring the Mysteries of the Gaia Hypothesis Date
Q: What is the Gaia Hypothesis, and when was it first proposed?
A: The Gaia Hypothesis, put forward by scientist James Lovelock, suggests that the Earth functions as a self-regulating organism. It was introduced to the world in the early 1970s, captivating minds with its innovative perspective on the interconnectedness of life on our planet.
Q: Why is the Gaia Hypothesis significant in understanding Earth’s ecosystems?
A: The Gaia Hypothesis challenges traditional views of Earth as a passive environment by proposing that living organisms and their surroundings are closely intertwined, forming a complex, self-regulating system. This idea revolutionizes the way we perceive and study ecosystems, highlighting the delicate balance that sustains life on Earth.
Q: How has the Gaia Hypothesis influenced environmental science and sustainability efforts?
A: By recognizing the Earth as a dynamic and interconnected entity, the Gaia Hypothesis has inspired researchers, policymakers, and activists to adopt a more holistic approach to environmental issues. It underscores the importance of preserving biodiversity, minimizing pollution, and promoting sustainable practices to maintain the planet’s health and well-being.
Q: Can the Gaia Hypothesis date help guide future conservation efforts?
A: Understanding the Gaia Hypothesis date can serve as a compass for conservationists and environmentalists, emphasizing the need to protect Earth’s intricate web of life. By acknowledging the interdependence of all living organisms and their environments, we can strive to create a more sustainable and harmonious relationship with the planet.
Q: What are some criticisms of the Gaia Hypothesis, and how has it evolved over time?
A: While the Gaia Hypothesis has sparked dialogue and exploration in the scientific community, it has also faced criticism for its anthropomorphic implications and lack of empirical evidence. Over the years, the hypothesis has evolved to incorporate new research findings and perspectives, enriching our understanding of Earth’s complex ecosystems and the delicate balance they maintain.
In Conclusion
As we delve into the intriguing world of the Gaia hypothesis and its influence on our understanding of the Earth as a living organism, it becomes clear that the concept of Gaia continues to spark curiosity and debate among scholars and nature enthusiasts alike. From its inception to its evolution over time, the Gaia hypothesis challenges us to reconsider our relationship with the planet we call home. Whether you are a skeptic or a believer, one thing remains certain – the Gaia hypothesis invites us to ponder the interconnectedness of all life on Earth and the delicate balance that sustains our existence. Let us continue to explore, question, and appreciate the wonder of Gaia in all its complexity.


0 Comments