In the intricate dance of Earth’s ecosystems, the Gaia Hypothesis emerges as a fascinating concept that delves into the interconnectedness of life and the environment. Through the lens of negative feedback, this theory unveils a symphony of balance and harmonious regulation within our planet’s delicate web of existence. Let’s embark on a journey into the realms of Gaia and explore how the intricate interplay of feedback mechanisms orchestrates the equilibrium of our biosphere.
Table of Contents
- Exploring the Link Between Gaia Hypothesis and Negative Feedback Mechanisms
- Unveiling the Intricacies of Negative Feedback in Gaia Hypothesis
- Practical Applications of Negative Feedback within the Gaia Framework
- Enhancing Environmental Sustainability Through Negative Feedback Systems
- Q&A
- In Retrospect
Exploring the Link Between Gaia Hypothesis and Negative Feedback Mechanisms
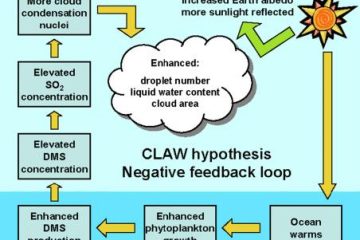
The Gaia hypothesis proposes that the Earth functions as a self-regulating system, maintaining conditions suitable for life. This intriguing concept suggests that the planet behaves like a single organism, with various interconnected feedback mechanisms at play.
<p>One fascinating aspect of the Gaia hypothesis is its connection to negative feedback mechanisms. Negative feedback loops help stabilize systems by counteracting any deviations from equilibrium. In the context of Earth's ecosystems, these feedback mechanisms play a crucial role in maintaining balance and sustainability over time.</p>
Unveiling the Intricacies of Negative Feedback in Gaia Hypothesis
In the realm of environmental science, the concept of negative feedback mechanisms plays a critical role in the Gaia Hypothesis. This hypothesis, first proposed by James Lovelock in the 1970s, suggests that the Earth functions as a self-regulating system where living organisms interact with the non-living components of the planet to maintain optimal conditions for life.
At the core of the Gaia Hypothesis lies the intricate web of interactions that result in feedback loops. Negative feedback loops within this framework serve to stabilize the Earth’s environment by dampening any deviations from the norm. By exploring these feedback mechanisms, we gain a deeper understanding of how the Earth maintains its delicate balance and sustains life as we know it.
Practical Applications of Negative Feedback within the Gaia Framework
Within the Gaia framework, negative feedback plays a crucial role in maintaining balance and stability in natural ecosystems. By understanding how negative feedback mechanisms function within the context of the Gaia hypothesis, we can appreciate the intricate web of interconnections that sustain life on Earth. **Negative feedback loops** act as self-regulating systems, ensuring that changes in one part of the ecosystem are counteracted to prevent drastic shifts that could disrupt the delicate equilibrium.
One practical application of negative feedback within the Gaia framework is evident in the regulation of atmospheric oxygen levels by living organisms. Through processes such as photosynthesis and respiration, plants and animals contribute to a harmonious cycle that helps maintain the optimal composition of gases in the atmosphere. This intricate interplay showcases the interconnectedness of all living beings and their vital role in sustaining the Earth’s delicate ecosystem.
| Key Point | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Photosynthesis | Plants absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen, contributing to the regulation of atmospheric gases. |
| Respiration | Animals consume oxygen and release carbon dioxide, completing the cycle and maintaining balance. |

Enhancing Environmental Sustainability Through Negative Feedback Systems
Negative feedback systems play a significant role in contributing to environmental sustainability by promoting equilibrium and stability within ecosystems. The Gaia hypothesis, an intriguing concept introduced by James Lovelock, suggests that the Earth functions as a complex system that regulates and maintains environmental conditions to support life. In this hypothesis, the planet acts as a self-regulating entity that adjusts various processes to ensure optimal conditions for the existence of diverse organisms.
Implementing negative feedback mechanisms can help mitigate environmental impacts such as climate change, biodiversity loss, and pollution. By utilizing feedback loops to detect changes in environmental conditions and initiate corrective actions, ecosystems can adapt and maintain a balance conducive to sustaining life. Through the application of innovative technologies and ecological practices, we can work towards creating a harmonious relationship between human activities and the natural world, fostering a more sustainable future for generations to come. Let’s embrace the power of negative feedback systems to protect our planet and preserve its delicate balance.
Q&A
Q: Is the Gaia Hypothesis an example of negative feedback in the environment?
A: Indeed, the Gaia Hypothesis, proposed by scientist James Lovelock, suggests that the Earth functions as a self-regulating system similar to a living organism. In this intricate system, negative feedback mechanisms play a crucial role in maintaining equilibrium. Just like a thermostat moderates temperature in a house, negative feedback loops within the Earth’s systems work to stabilize and empower sustainability.
In Retrospect
In conclusion, the Gaia hypothesis stands as a fascinating testament to the intricate balance of our planet Earth—a delicate dance of negative feedback mechanisms that sustain life as we know it. By delving into the interconnected web of nature’s checks and balances, we gain a deeper appreciation for the resilience and harmony of our shared biosphere. As we continue to explore the implications of this hypothesis, let us remember that our actions have the power to either disrupt or enhance this delicate equilibrium. Embracing a mindset of stewardship and respect towards our planet may prove to be the key in safeguarding the future of all living beings on Earth. Join us in our journey towards understanding and nurturing the intricate tapestry of Gaia—a tapestry where every thread, every interaction, plays a vital role in maintaining the beauty and balance of our cherished home.


0 Comments