Table of Contents
- Origins of the Gaia Hypothesis and Its Intellectual Roots
- James Lovelocks Scientific Vision and Contributions to Earth Science
- Interpreting the Gaia Hypothesis: A Holistic View of Earth
- Gaias Influence on Modern Environmental Thought and Policy
- Recommendations for Further Reading on Lovelocks Gaia Theory
- Q&A
- The Conclusion

Origins of the Gaia Hypothesis and Its Intellectual Roots
Conceived in the vibrant intellectual milieu of the 1960s, the idea that Earth functions as an interconnected system was first articulated by British scientist James Lovelock. While consulting for NASA, Lovelock developed an innovative perspective: Earth, with its myriad ecosystems, operates akin to a self-regulating organism. This groundbreaking concept took inspiration from a wide array of intellectual influences, drawing from fields as varied as atmospheric science, cybernetics, and systems theory. Lovelock and his collaborator, microbiologist Lynn Margulis, postulated that living organisms interact with their inorganic surroundings on Earth to form a synergistic and self-regulating complex system that helps to maintain and perpetuate the conditions for life on the planet.
The intellectual roots of this theory can be traced back to earlier scientific works that began to fuse notions of organismic and holistic ecology. Visionaries such as Alexander von Humboldt, a key figure in the field of biogeography, laid the groundwork by emphasizing the interconnectedness of nature. Cybernetics, the study of systems, control, and communication in animals and machines, further influenced Lovelock’s thinking. This interdisciplinary approach was instrumental in forming the basis of what would eventually become his life’s work. His hypothesis was not just about the science of life, but about understanding life in relation to Earth’s systems.
| Influences | Description |
|---|---|
| Atmospheric Science | Provided insights into Earth’s systemic homeostasis. |
| Cybernetics | Inspired concepts of feedback loops and regulatory mechanisms. |
| Biogeography | Influenced by Humboldt, emphasized ecosystem connections. |
Despite initial skepticism, the Gaia Hypothesis gained traction, partly due to its eloquent integration of Earth science and biological insight. It has gradually evolved, finding a significant place in discussions about climate change, environmental sustainability, and planetary health. Lovelock’s framing of Earth as a complex, interwoven entity not only transformed scientific discourse but also inspired a new generation to view our planet as a delicately balanced ecosystem to be cherished and protected.
James Lovelocks Scientific Vision and Contributions to Earth Science
James Lovelock’s groundbreaking scientific insights have reshaped our understanding of Earth as a living system. Central to his contributions is the Gaia Hypothesis, which proposes that the Earth operates as a self-regulating complex system. This theory, which he developed alongside microbiologist Lynn Margulis, suggests that living organisms interact with their inorganic surroundings to maintain conditions conducive to life. Lovelock’s visionary perspective extends beyond mere ecological processes; he envisions Earth itself as a single, vast organism, responding to and correcting imbalances to sustain life.
- Interconnected Systems: He highlighted the interdependence within ecosystems, where each component impacts the others, emphasizing the delicate balance necessary for ecological stability.
- Holistic Approach to Climate Change: Lovelock’s work brought attention to how climate change could disrupt Earth’s self-regulating systems, advocating for a comprehensive perspective when addressing environmental issues.
- Advancements in Atmospheric Science: His research on atmospheric gases and their interaction with both living organisms and the environment significantly increased our understanding of environmental science.
| Concept | Significance |
|---|---|
| Gaia Hypothesis | A framework viewing Earth as a synergistic and self-regulating system. |
| Homeostasis | Demonstrates Earth’s ability to maintain a stable climate and surface temperature. |
| Biotic Feedback | Explains how life forms contribute to global processes like atmospheric composition. |
Lovelock’s perspectives have sparked broad scientific debates and inspired subsequent research across various fields, from geology to biology. While the Gaia Hypothesis initially faced skepticism, it gained traction as it intertwined disciplines, urging scientists to consider the planet as an interdependent whole rather than isolated systems. By inspiring a generation of thinkers to appreciate the Earth in a new light, Lovelock not only enriched scientific thought but also imbued it with an element of wonder and responsibility towards preserving our planet’s vitality for future generations.
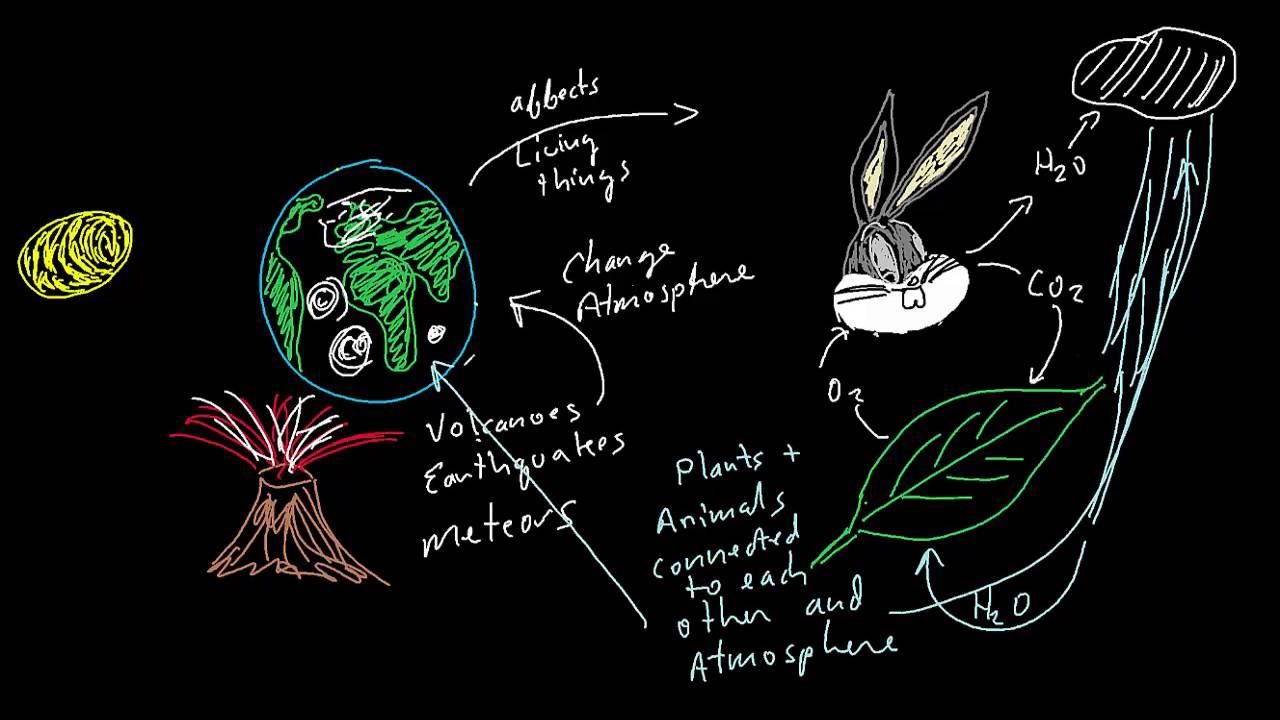
Interpreting the Gaia Hypothesis: A Holistic View of Earth
- Feedback Loops: These mechanisms ensure stability and balance within the Earth’s climate and ecosystems.
- Homeostasis: Similar to living beings, the Earth strives to maintain internal stability amidst external changes.
- Interdependency: Each species, whether large or microscopic, plays a role in sustaining the greater ecological equilibrium.
| Activity | Effect on Gaia |
|---|---|
| Deforestation | Disruption in carbon cycling |
| Pollution | Alteration of natural feedback loops |
| Fossil Fuels | Increases in atmospheric greenhouse gases |

Gaias Influence on Modern Environmental Thought and Policy
The Gaia Hypothesis, proposed by James Lovelock, has had a profound impact on shaping modern environmental ideologies. This theory suggests that Earth functions as a self-regulating entity, where the biotic and abiotic components interact to sustain life. This paradigm shift emphasized the interconnectedness of ecosystems, influencing environmental policies that prioritize sustainability. As policymakers embraced this holistic view, it led to the creation of more comprehensive environmental protection laws aiming to maintain ecological balance.
- Renewable Energy Policies: Inspired by the Gaia Hypothesis, governments worldwide have increased investments in renewable energy sources, reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
- Biodiversity Preservation: Recognizing the importance of biodiversity for maintaining Gaia’s balance, policies now emphasize the protection of endangered species and ecosystems.
- Climate Change Initiatives: Viewing Earth as a cohesive system has strengthened global commitments to combat climate change through agreements like the Paris Accord.
The integration of Gaia’s philosophy into environmental thought extends beyond policy to educational and community initiatives. Educational curricula increasingly incorporate concepts of planetary health, encouraging students to consider their actions in the context of global ecosystems. Community-led projects, such as urban green spaces and local conservation efforts, often draw upon Gaia-inspired principles of sustainability and harmony with nature. By nurturing a collective environmental consciousness, these initiatives reflect a growing recognition of humanity’s role within Lovelock’s living Earth model.

Recommendations for Further Reading on Lovelocks Gaia Theory
Diving deeper into the captivating world of Gaia Theory as articulated by James Lovelock, there exists a treasure trove of literature that expands on the ecological and philosophical implications of this hypothesis. Lovelock’s own works provide an essential foundation. His books, such as Gaia: A New Look at Life on Earth and The Revenge of Gaia, shed light on the intricate balance of life and ecosystems, offering insights into the self-regulating behavior of our planet.
- Margulis’s Contributions: Delve into Lynn Margulis’s collaborative efforts with Lovelock, which emphasize the role of symbiotic relationships within the Gaia framework. Her writings offer a biological perspective that complements Lovelock’s environmental focus.
- Philosophical Exploration: To explore the ethical and philosophical dimensions, consider reading The Ages of Gaia by Lovelock, where he addresses how humanity can adapt to Gaia’s dynamic processes.
- Scientific Critiques and Support: Engage with works like The Vanishing Face of Gaia for a critical view, discussing both challenges and support within the scientific community regarding Lovelock’s ideas.
For a comprehensive exploration, these texts are invaluable:
| Book Title | Author | Focus Area |
|---|---|---|
| Gaia: A New Look at Life on Earth | James Lovelock | Core Concepts |
| Symbiotic Planet | Lynn Margulis | Biological Perspective |
| The Ages of Gaia | James Lovelock | Philosophical Insights |



0 Comments