In the vast tapestry of theories that seek to unravel the mysteries of our planet Earth, one concept stands out like a beacon of interconnectedness and harmony – the Gaia Hypothesis. This mind-bending idea proposes that our planet is not just a collection of rocks, water, and air but a living, breathing organism in its own right. Join us on a journey through the essence of the Gaia Hypothesis, as we delve into its core principles and implications for our understanding of the intricate web of life that surrounds us. Let’s embark on a voyage of discovery, where science meets spirituality, and the Earth reveals its secrets in the most fascinating of ways.
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Gaia Hypothesis: A Complete Overview
- Exploring the Interconnectedness of Earth’s Systems
- Implications of Gaia Hypothesis for Environmental Conservation
- Practical Steps to Embrace Gaia Hypothesis in Daily Life
- Q&A
- The Way Forward
Understanding the Gaia Hypothesis: A Complete Overview
The Gaia Hypothesis proposes that the Earth is a self-regulating system where living organisms interact with their surroundings to maintain an optimal environment for life. This idea, developed by James Lovelock in the 1970s, suggests that the Earth functions as a single organism that works to sustain life through complex feedback mechanisms.
Key points of the Gaia Hypothesis include the interconnectedness of all living and non-living components of the planet, the idea that life has actively contributed to shaping the Earth’s environment, and the concept of Earth as a dynamic and evolving system. By viewing the Earth as a unified and self-regulating entity, the Gaia Hypothesis challenges traditional views of the planet as a passive backdrop for life to unfold.

Exploring the Interconnectedness of Earth’s Systems
Just as the roots of a tree intertwine with the soil, Earth’s systems are intricately connected, forming a delicate web of life that sustains our planet. The Gaia Hypothesis, proposed by scientist James Lovelock, suggests that Earth functions as a self-regulating organism where all living and non-living components interact to maintain a stable environment conducive to life.
From the oceans to the atmosphere, every element of the Earth system plays a vital role in maintaining the delicate balance necessary for life to thrive. The exchange of energy, nutrients, and gases between the atmosphere, hydrosphere, lithosphere, and biosphere highlights the interconnectedness of Earth’s systems, showcasing how each component influences and depends on the others in a harmonious dance of sustainability.
Implications of Gaia Hypothesis for Environmental Conservation
The Gaia Hypothesis proposes that the Earth functions as a single, self-regulating organism where living organisms interact with their inorganic surroundings to form a complex system that maintains the conditions necessary for life. This interconnectedness highlights the importance of viewing the Earth as a unified entity where everything is interdependent. By understanding the implications of this hypothesis, we can revolutionize our approach to environmental conservation.
Key :
- Interconnectedness: Recognizing the interconnected nature of all living beings and their environment emphasizes the need for holistic conservation efforts.
- Symbiotic Relationships: Understanding how different species coexist in delicate balances highlights the importance of preserving biodiversity for the overall health of the planet.
- Regenerative Systems: Viewing the Earth as a self-regulating system encourages the development of sustainable practices that mimic natural processes to ensure long-term environmental health.
Table:
| Conservation Approach | Impact |
|---|---|
| Restoration of Ecosystems | Promotes biodiversity and ecological resilience. |
| Sustainable Resource Management | Prevents depletion of resources and supports long-term environmental health. |
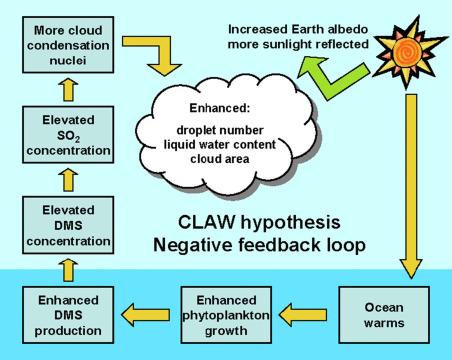
Practical Steps to Embrace Gaia Hypothesis in Daily Life
Incorporating the Gaia Hypothesis into your daily routine can be a transformative experience that connects you deeply with the environment around you. To start embracing this concept effortlessly, consider simple yet impactful actions such as **daily mindfulness exercises** in nature to foster a stronger bond with the Earth. By taking walks in the forest or practicing meditation outdoors, you can enhance your awareness of the interconnectedness of all living beings.
Another practical step is to reduce your carbon footprint by making sustainable choices in your lifestyle, such as opting for eco-friendly products, reducing waste, and supporting local farmers and businesses. Small changes like using reusable bags, minimizing energy consumption, and participating in community environmental initiatives can contribute to the well-being of the planet in alignment with the principles of the Gaia Hypothesis. By incorporating these practices into your daily life, you not only benefit the Earth but also cultivate a sense of harmony and respect for the natural world.
Q&A
Q&A: Gaia Hypothesis Summary
Q: What is the Gaia Hypothesis all about?
A: The Gaia Hypothesis proposes that the Earth is a self-regulating system where living organisms interact with their inorganic surroundings to maintain conditions suitable for life.
Q: Who proposed the Gaia Hypothesis?
A: The Gaia Hypothesis was first proposed by scientist James Lovelock and biologist Lynn Margulis in the 1970s.
Q: How does the Gaia Hypothesis differ from traditional views of Earth?
A: Unlike traditional views that consider Earth as a passive environment, the Gaia Hypothesis suggests that the planet functions as a single, self-regulating organism.
Q: What are some key concepts associated with the Gaia Hypothesis?
A: Concepts linked to the Gaia Hypothesis include homeostasis, feedback mechanisms, and the idea that life actively participates in shaping Earth’s environment.
Q: What evidence supports the Gaia Hypothesis?
A: Evidence such as the regulation of atmospheric oxygen levels and the stabilization of ocean salinity provides support for the idea that life plays a role in maintaining Earth’s habitable conditions.
Q: How has the Gaia Hypothesis influenced scientific thinking?
A: The Gaia Hypothesis has sparked discussions about Earth’s interconnectedness and the impact of human activities on the planet, leading to a deeper understanding of environmental issues.
Q: What are some criticisms of the Gaia Hypothesis?
A: Critics argue that the Gaia Hypothesis anthropomorphizes Earth and may oversimplify the complexities of ecosystems, challenging the idea of the Earth as a single, self-regulating organism.
Q: In what ways can the Gaia Hypothesis inspire changes in how we view and interact with the environment?
A: The Gaia Hypothesis can inspire a shift towards viewing Earth as a living system worthy of respect and care, promoting sustainability and a sense of interconnectedness with nature.
The Way Forward
In conclusion, the Gaia hypothesis offers a fascinating perspective on the interconnectedness of life on Earth. By viewing our planet as a self-regulating system, it prompts us to reflect on our role in maintaining the balance of this intricate web of life. As we contemplate the beauty and complexity of Gaia, may we find inspiration to nurture and protect our precious home for generations to come. Embrace the harmony of Gaia and let it guide us towards a more sustainable and symbiotic relationship with our planet. Thank you for exploring this insightful summary of the Gaia hypothesis – may our journey towards a greener future be guided by the wisdom of this profound theory.



0 Comments