Delve into the lush world of plant ecology, where nature’s intricate tapestry weaves together a symphony of life. From towering forests to delicate meadows, examples of plant ecology abound, each telling a unique story of survival and adaptation. Join us on a journey through the botanical wonders of the natural world, as we uncover the fascinating interplay between plants, their environment, and the diverse ecosystems they call home. Let’s embark on a quest to explore the beauty and complexity of plant ecology through captivating examples that showcase the resilience and diversity of our green companions on this planet.
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Role of Soil Microorganisms in Plant Ecology
- Exploring Mutualistic Relationships in Plant Communities
- Unraveling the Impact of Climate Change on Plant Diversity
- Implementing Sustainable Practices to Support Plant Ecology
- Q&A
- Insights and Conclusions
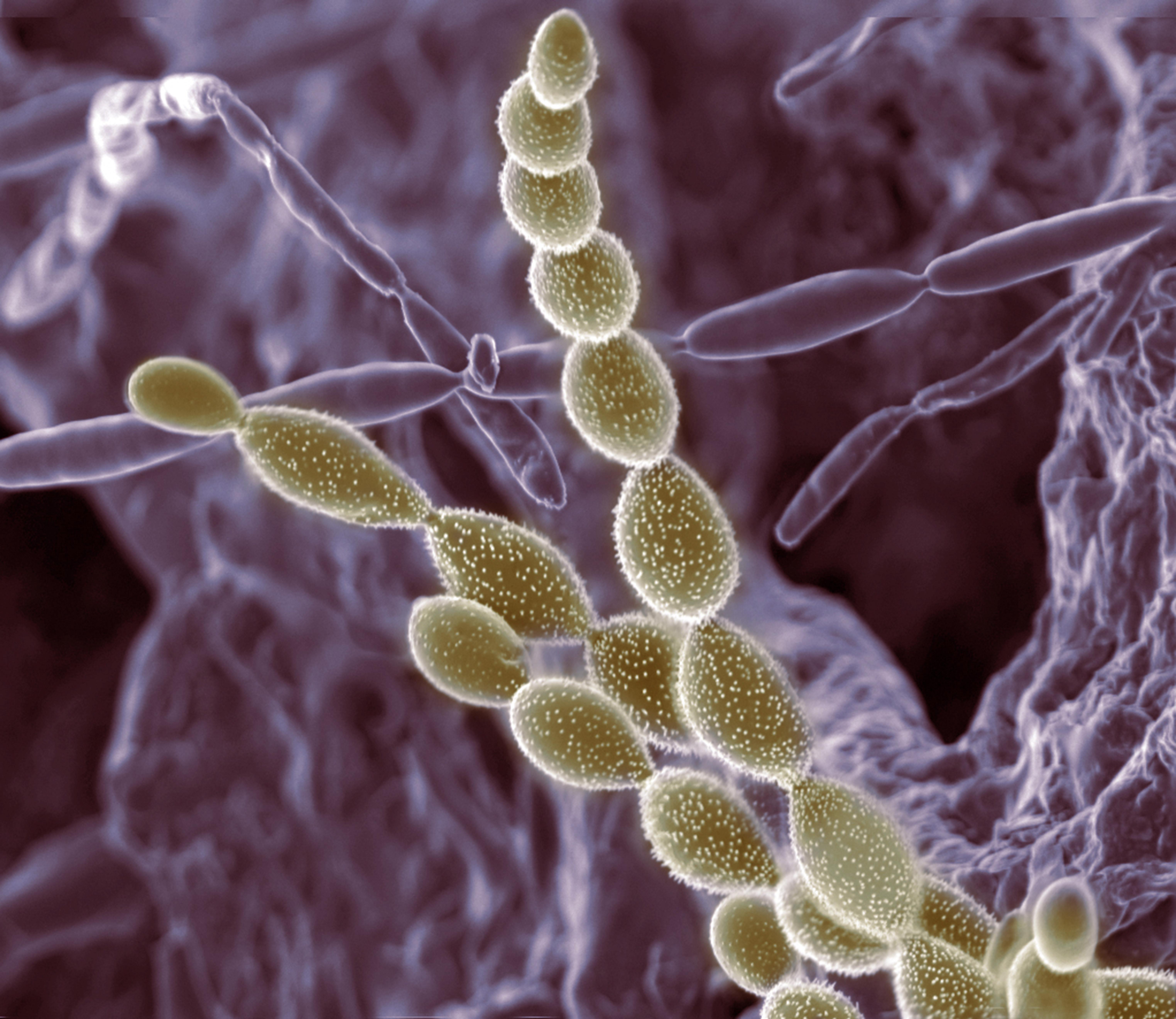
Understanding the Role of Soil Microorganisms in Plant Ecology
In the intricate world of plant ecology, soil microorganisms play a vital yet often-underestimated role in shaping the environment where plants thrive. These tiny organisms, including bacteria, fungi, and protozoa, form a dynamic network beneath our feet, interacting with plant roots in fascinating ways we are only beginning to understand.
Here are some intriguing examples:
- Mycorrhizal Fungi: These beneficial fungi form mutualistic relationships with plant roots, aiding in nutrient uptake and water absorption.
- Nitrogen-Fixing Bacteria: Transforming atmospheric nitrogen into a form usable by plants, these bacteria play a key role in enriching the soil with essential nutrients.
- Decomposers: Break down organic matter, returning vital nutrients to the soil for plant use.
- Pathogens: While detrimental in excess, they also help regulate plant populations and promote diversity.
By delving into the intricate interactions between plants and soil microorganisms, we uncover a fascinating world where every tiny organism has a part to play in the intricate tapestry of plant ecology. Understanding and appreciating their roles can lead to sustainable practices that benefit both plants and the environment as a whole.
Exploring Mutualistic Relationships in Plant Communities
In the intricate world of plant ecology, mutualistic relationships play a crucial role in sustaining diverse plant communities. Mutualistic relationships, where two organisms benefit from each other’s presence, can be seen in various fascinating ways within plant ecosystems.
One captivating example involves mycorrhizal fungi and plants working together underground. These symbiotic partners form a mutually beneficial relationship where the fungi help the plants absorb essential nutrients like phosphorus and nitrogen from the soil, while the plants provide sugars to the fungi through photosynthesis. This intricate underground collaboration highlights the interconnectedness and co-dependency that exist within plant communities, showcasing the beauty of nature’s intricate web of life.
th {background-color: #f2f2f2;
}
td {
text-align: center;
}
| Plant Species | Mycorrhizal Fungi Partner |
|---|---|
| Rhododendron | Armillaria mellea |
| Sunflower | Rhizophagus intraradices |
| Pine tree | Suillus luteus |
| Potato | Glomus intraradices |
Unraveling the Impact of Climate Change on Plant Diversity
In the intricate web of nature, the effects of climate change on plant diversity are becoming increasingly pronounced. As temperatures rise and weather patterns shift, plant species are facing unprecedented challenges in adapting to these new environmental conditions. **Increased frequency of extreme weather events** such as droughts and floods can disrupt ecosystems, leading to shifts in plant populations and potential extinctions of vulnerable species.
Moreover, altered growing seasons and habitats are forcing plants to migrate or face local extinction, impacting not only the flora itself but also the animals and insects that depend on them for survival. The delicate balance of plant communities is being reshaped, highlighting the urgent need for conservation efforts and sustainable environmental practices to safeguard the rich tapestry of plant diversity for future generations.
| Plant Species | Climate Impact |
|---|---|
| Rosemary | Reduced growth due to increased heat stress |
| Maple Trees | Shifting habitats as temperatures rise |
| Sunflowers | Altered flowering patterns due to changing seasons |

Implementing Sustainable Practices to Support Plant Ecology
In the realm of promoting plant ecology through sustainable practices, small changes can yield significant benefits. One such example is enriching the soil with organic matter like compost and mulch to improve nutrient levels and overall soil health. **By enhancing the soil composition naturally, plants thrive better, fostering a healthier ecosystem for all.**
Another impactful practice is the strategic planting of native vegetation to support local biodiversity. Native plants are well adapted to the specific environmental conditions of an area, requiring less water and maintenance compared to non-native species. These plant choices not only conserve water but also provide habitats for local wildlife, promoting a balanced and sustainable ecosystem.
Q&A
Q: What is plant ecology, and why is it essential?
A: Plant ecology is a branch of biology that focuses on the relationships between plants and their environment. It delves into how plants interact with other organisms and the physical world around them. Understanding plant ecology is crucial as it provides insights into ecosystem dynamics, biodiversity, and the impact of human activities on the environment.
Q: Can you give examples of plant ecology in action?
A: Absolutely! One fascinating example of plant ecology is the mutualistic relationship between plants and pollinators. Bees, butterflies, and other pollinators help plants reproduce by transferring pollen between flowers, aiding in the production of fruits and seeds. Another example is plant succession, where different plant species replace each other over time in a specific area, showcasing the dynamic nature of plant communities.
Q: How do plants adapt to their surroundings?
A: Plants have evolved diverse adaptations to thrive in various environments. For instance, desert plants like cacti have developed water-storing tissues and reduced leaf surfaces to survive in arid conditions. In contrast, aquatic plants have specialized structures to extract oxygen from water and support themselves in aquatic habitats.
Q: What role do plants play in the ecosystem?
A: Plants play a multitude of crucial roles in ecosystems. They serve as primary producers, converting sunlight into energy through photosynthesis and forming the base of the food chain. Additionally, plants help regulate the climate by absorbing carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen, contributing to air quality and the carbon cycle.
Q: How can individuals contribute to plant ecology conservation?
A: Individuals can contribute to plant ecology conservation by supporting native plant species, practicing sustainable gardening methods, and advocating for the protection of natural habitats. Additionally, participating in community initiatives such as tree plantings and habitat restoration projects can make a positive impact on plant biodiversity and ecosystem health.
Insights and Conclusions
As we explore the fascinating world of plant ecology examples, we are reminded of the intricate dance of life that unfolds in every corner of our planet. From the lush rainforests to the barren deserts, plants play a vital role in shaping our environment and supporting diverse ecosystems. By understanding and appreciating these examples, we gain a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of all living things. So, let’s continue to marvel at the wonders of plant ecology and strive to protect and preserve the natural world for future generations to come. Embrace the beauty of nature and let it inspire you to make a positive impact on our shared world.



0 Comments