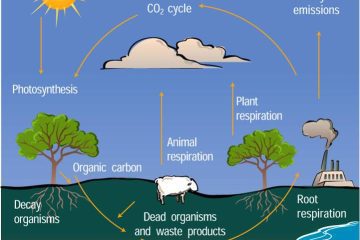
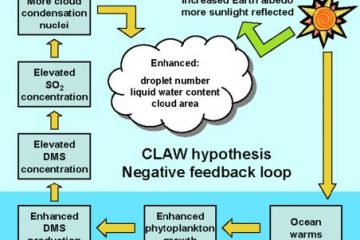
Gaia hypothesis
gaia hypothesis geography
The Gaia Hypothesis intertwines the realms of geography and ecology, suggesting Earth functions as a self-regulating system. This concept prompts us to reconsider how landscapes, climates, and life forms collaborate in maintaining the planet’s delicate balance.