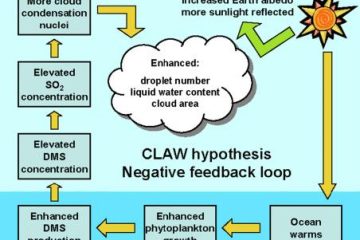
Gaia hypothesis
gaia hypothesis simplified
The Gaia Hypothesis posits that Earth functions as a single, self-regulating system. It suggests that living organisms interact with their inorganic surroundings to maintain conditions suitable for life, emphasizing the interconnectedness of all ecosystems.