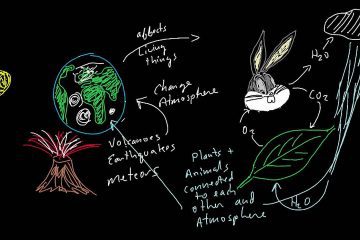
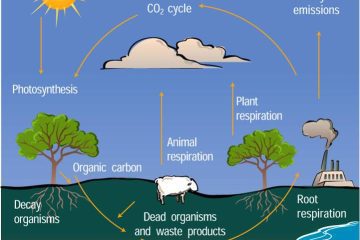
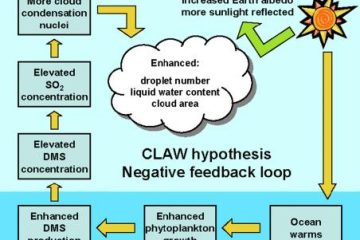
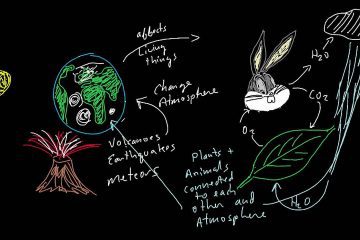
Planetary ecology
planetary ecosystem definition
A planetary ecosystem encompasses the intricate web of life and environments on Earth, where diverse species interact within their habitat. This interconnected system highlights how each organism contributes to the balance of nature, shaping our world.