James Lovelock
gaia hypothesis james lovelock pdf
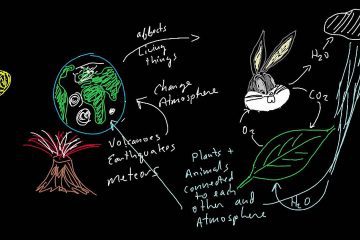
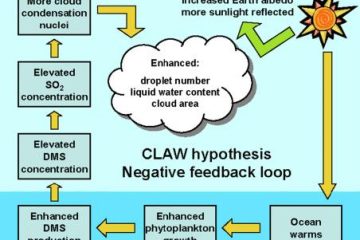
The Gaia Hypothesis, introduced by James Lovelock, posits that Earth’s biological and inorganic components form a self-regulating system. This interconnectedness emphasizes the delicate balance of life, urging us to rethink our relationship with nature. Discover more in his insightful PDF.