James Lovelock
james lovelock dunedin
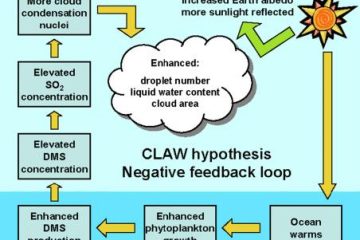
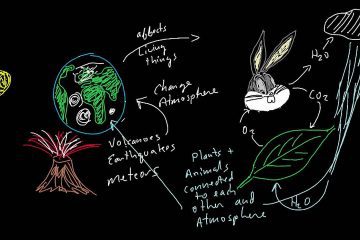
James Lovelock, the pioneering scientist, and environmentalist, left an indelible mark on Dunedin during his visit. His insights into Gaia theory sparked discussions on ecology and sustainability, inspiring a new generation to contemplate our planet’s delicate balance.