Gaia hypothesis
gaia hypothesis origins
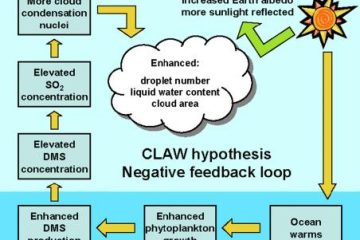
The Gaia Hypothesis, conceived by James Lovelock in the 1970s, posits that Earth functions as a self-regulating system. This revolutionary idea blends science with philosophy, suggesting that living organisms and their environment are intricately interconnected.